Shunlitongda Electronics Technology (Dongguan) Co., Ltd.
 +86 13826913652
+86 13826913652
 slthardware@outlook.com
slthardware@outlook.com
Discussion on the Technology and Application of Injection Molding Hardware Products
plastic-metal injection molding products (also known as insert molding or metal-plastic hybrid parts):
1. Technological & Process Innovations
Popularity of Insert Molding:
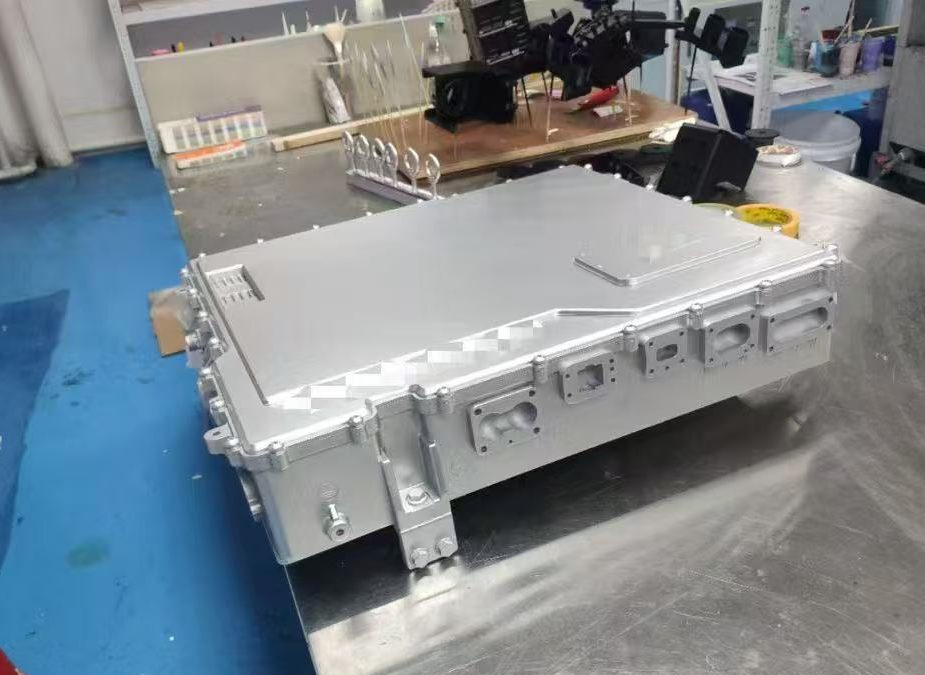
Metal parts (e.g., screws, bearings, inserts) are molded directly into plastic, reducing assembly steps and improving structural strength and precision (common in automotive and electronics).
Micro-Molding with Precision Metal Parts:
Tiny metal components (e.g., SIM card trays, micro connectors) combined with high-precision plastic, demanding advanced molds and machines.
Multi-Material Molding:
Combining metals with engineering plastics (e.g., PA, PPS) for strength and lightweighting (e.g., car door handles, gearbox components).
2. Material Science & Performance Optimization
Metal-Plastic Interface Bonding:
Surface treatments (plating, laser etching, chemical coatings) to enhance adhesion and prevent delamination.
-High-Performance Plastics:
PEEK + metal inserts for high-temperature applications (aerospace), or conductive plastics + EMI shielding for electronics.
Eco-Friendly Materials:
Recyclable metals + bio-based plastics to meet circular economy demands.
3. Industry Applications & Market Trends
Automotive Lightweighting:
Hybrid metal-plastic structures (e.g., dashboard frames, battery housings) reduce weight while maintaining strength.
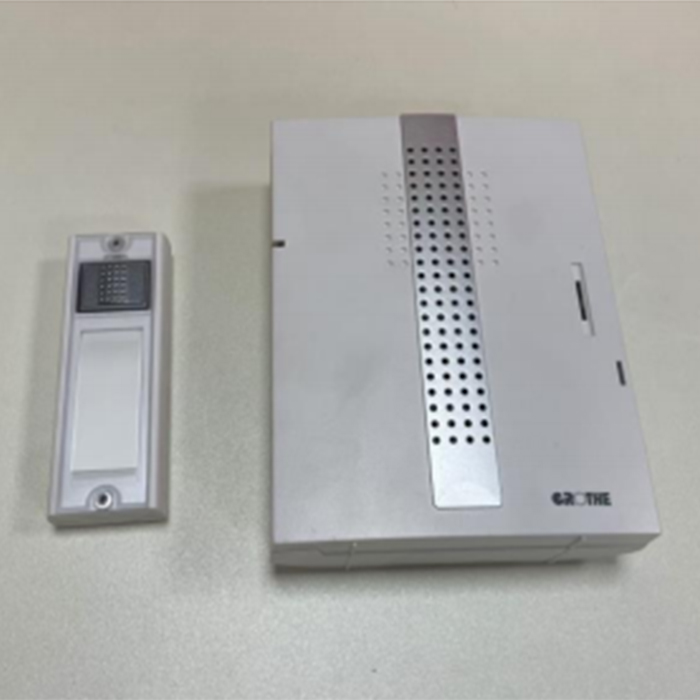
Consumer Electronics Integration:
Metal frames + plastic antenna designs (smartphones), waterproof structures in wearables.
Home Appliance Upgrades:
Seamless molding of metal hinges with plastic doors (refrigerators, washing machines) for durability and aesthetics.
4. Cost & Efficiency Challenges
Mold Complexity:
High-precision metal insert positioning requires error-proof molds, increasing upfront costs.
Automation Barriers:
Manual insert placement may limit efficiency; robotic or vision-guided systems are needed.
Yield Rate Issues:
Differential shrinkage (metal vs. plastic) causes warpage; solved via simulation (e.g., Moldflow) and process optimization.
5. Sustainability & Future Trends
Design for Disassembly:
Easier recycling (metal/plastic separation) to comply with regulations like WEEE.
3D-Printed Metal Inserts + Molding:
Enables low-volume customization (e.g., medical implant casings).
Smart Hybrid Products:
Metal sensors embedded in plastic (e.g., smart valves) for functional integration.
6. Common Problems & Solutions
Stress Cracking: Rounded edges or glass-fiber reinforcement at metal-plastic joints.
Corrosion Risk: Use stainless steel or passivated metal inserts.
Thermal Expansion Mismatch: Material selection or structural design to accommodate expansion.