Shunlitongda Electronics Technology (Dongguan) Co., Ltd.
 +86 13826913652
+86 13826913652
 slthardware@outlook.com
slthardware@outlook.com
Description
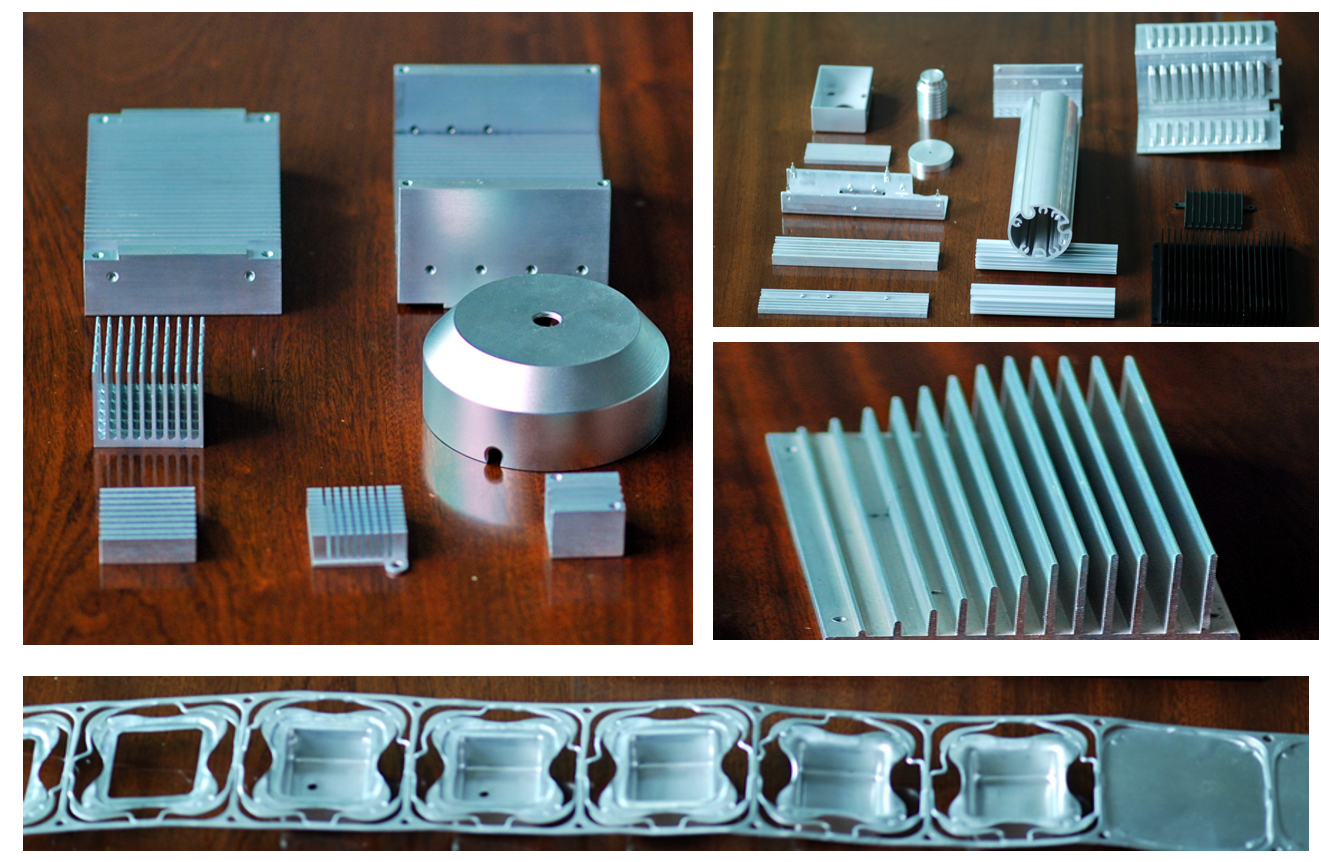
I. Types of Heat Sinks and Enhanced Technologies
| Type | Characteristics | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Passive Heat Sink | Fanless, relies on natural convection (aluminum fins) | Low-power devices (routers, LED lights) |
| Active Heat Sink | Uses fans for forced cooling (higher efficiency but consumes power) | Computer CPUs, graphics cards |
| Heat Pipe Cooler | Utilizes heat pipes for rapid heat transfer | High-performance laptops, servers |
| Liquid Cooler | Uses liquid circulation (quiet and efficient) | Overclocked PCs, data centers |
| Phase Change Cooler | Employs phase change materials (e.g., vapor chambers) | Smartphones, 5G base stations |
Enhancement Technologies:
-
Surface Treatment: Anodizing (improves emissivity), graphene coating (enhances thermal conductivity).
-
Structural Optimization: Fin density/shape design (e.g., vortex fins to increase turbulence).
2. Key Selection Parameters
-
Thermal Resistance (°C/W): Lower values indicate better cooling performance.
-
Material: Copper (faster heat transfer but costly) vs Aluminum (lightweight and cost-effective).
-
Air Pressure & Flow Rate (for active cooling): Fan performance must match cooling requirements.
Industry Trends:
-
Miniaturization: Ultra-thin heat sinks (for foldable smartphones).
-
Intelligent Control: Temperature-regulated fan speed adjustment.
-
Green Cooling: Fanless designs (reduce noise and power consumption).